Methods for workplace health promotion
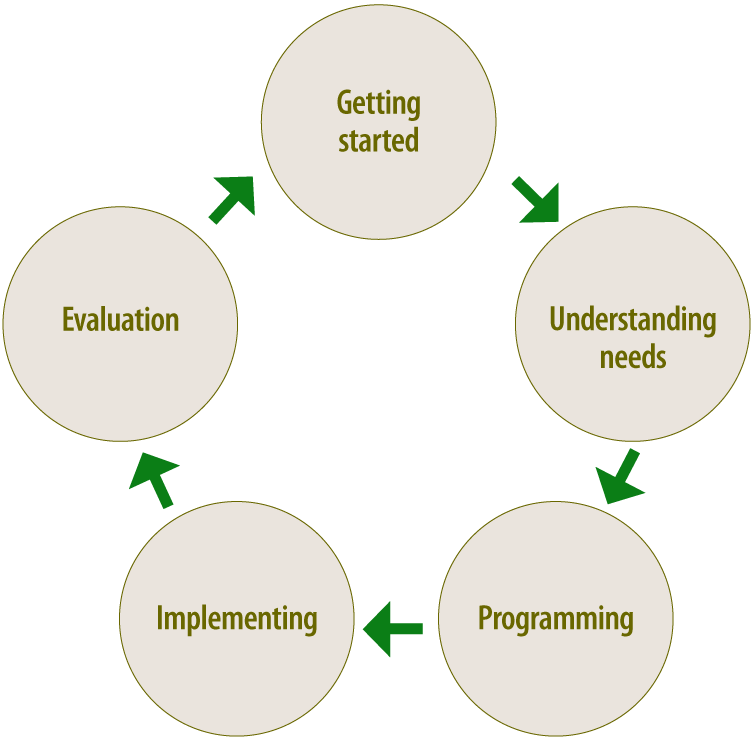
The implementation cycle
Implementing Workplace Health Promotion (WHP) is best done by following an implementation cycle like the one below:
- Getting started: Preparing the ground for the exercise intervention with the main stakeholders – employers, employees and others
- Understanding needs: Finding out stakeholders needs with regard to the exercise intervention. A recent tool to support needs analysis has been developed in the UK by Public Health England:
Workplace health needs assessment. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/workplace-health-needs-assessment.
- Programming: Deciding on the nature and setting up of the exercise intervention
- Implementing: Running and monitoring the programme
- Evaluation: Analysing monitoring data, identifying improvement measures
Principles of approach
Implementing exercise programmes in the workplace should incorporate a number of principles that will guarantee an ethical approach as well as increasing the chances of having a successful exercise programme. These principles are:
- Support from all levels of the organisation – WHP initiatives need to be supported by staff from all levels of the organisation. Where support from either management or employees is lacking, it becomes difficult or impossible to implement a programme. This means that effort that is spent gathering support before the programme commences is essential.
- Voluntary participation – Workers must be able to participate in in the WHP programme on a voluntary basis. They must be able to opt in or opt out of the programme at any stage. No sanctions should apply to any worker who does not participate or who opts out.
- Anonymity and confidentiality – Any data that is collected as part of the programme must be treated anonymously. Information on individuals should not be disclosed to any third party without the permission of the individual who has provided the data.
- Needs based programming – WHP should be based on the needs of individuals or groups. Tailoring interventions in this way improves their chances of successful take-up.
- Continuous improvement – Gathering information about the performance of the intervention provides a sound basis for improving its performance the next time. The intervention should take place within a continuous improvement cycle.
- Communications and feedback – communications and feedback are required at all stages of the programme with both the participants and the wider workforce in the organisation and with management. This enables expectations to be managed and provides feedback to all who have provided information to the project. Reporting on a formal basis to management allows for the programme to be embedded within the normal functioning of the organisation.
Tools
- Utilities:
- Print this page
- Send this page